ENEXSA continuously works with OEM of gas turbines and reciprocating engines to maintain and enlarge one of the world's largest collections of performance characteristics of gas turbines and reciprocating engines.
The user can perform in-depth thermodynamic analysis of the overall plant benefiting from the features of EBSILON®Professional, such as:
ENEXSA works with gas turbine and gas engine manufacturers to continually expand the ENEXSA libraries and create a valuable and "living" source of gas turbine and reciprocating engine performance data so that engineers worldwide can use reliable, first-hand data to analyze and improve CHP plants.
Get access to more than a thousand gas turbine performance curve sets.
Get access to over 180 reciprocating Engine performance curve sets.
The ENEXSA Gas Turbine Library is designed for the use within the EBSILON®Professional Component 106 "Gas Turbine (OEM GT)". The ENEXSA Gas Turbine Library covers the full range of industrial applications, from micro gas turbines to large H-class gas turbines. The performance data are supplied and approved by the respective OEM. Data updates are generated as soon as new models and/or performance updates become available.
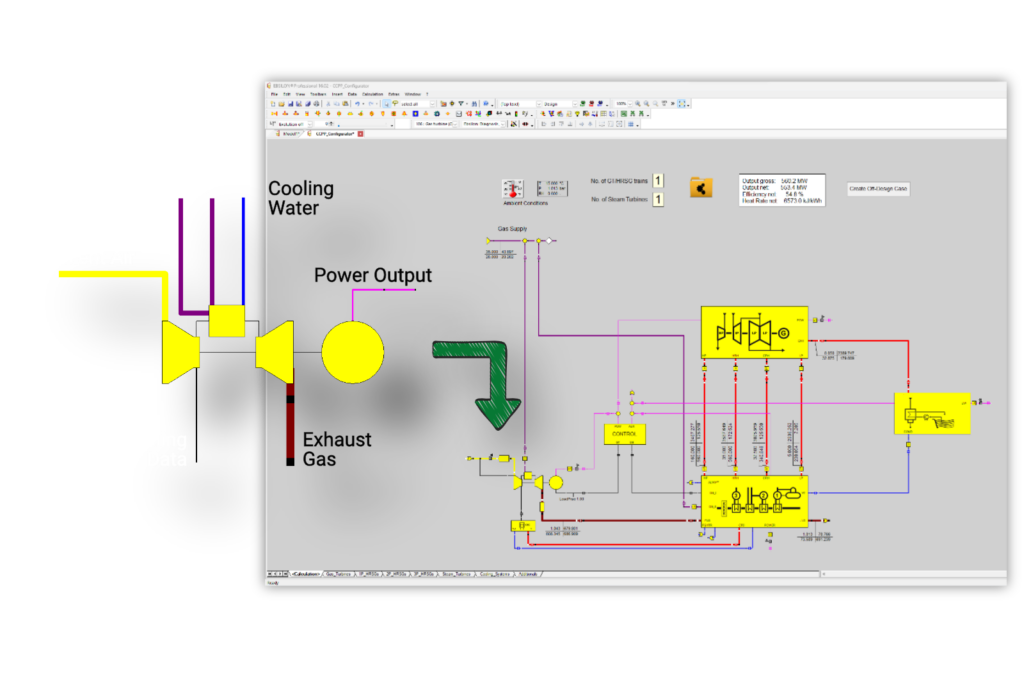
The performance characteristics of the gas turbine have a large impact on the subsequent HRSG and its steam cycle. Modern high-efficiency gas turbines also integrate with the water-steam cycle for fuel and/or air pre-heating, and in some cases the waste heat from the GT combustor and turbine are re-covered in the HRSG. The EBSILON model of the overall plant enables the user to evaluate these processes over the entire operating range of the plant based on the detailed off-design performance data supplied in the ENEXSA Gas Turbine Library.
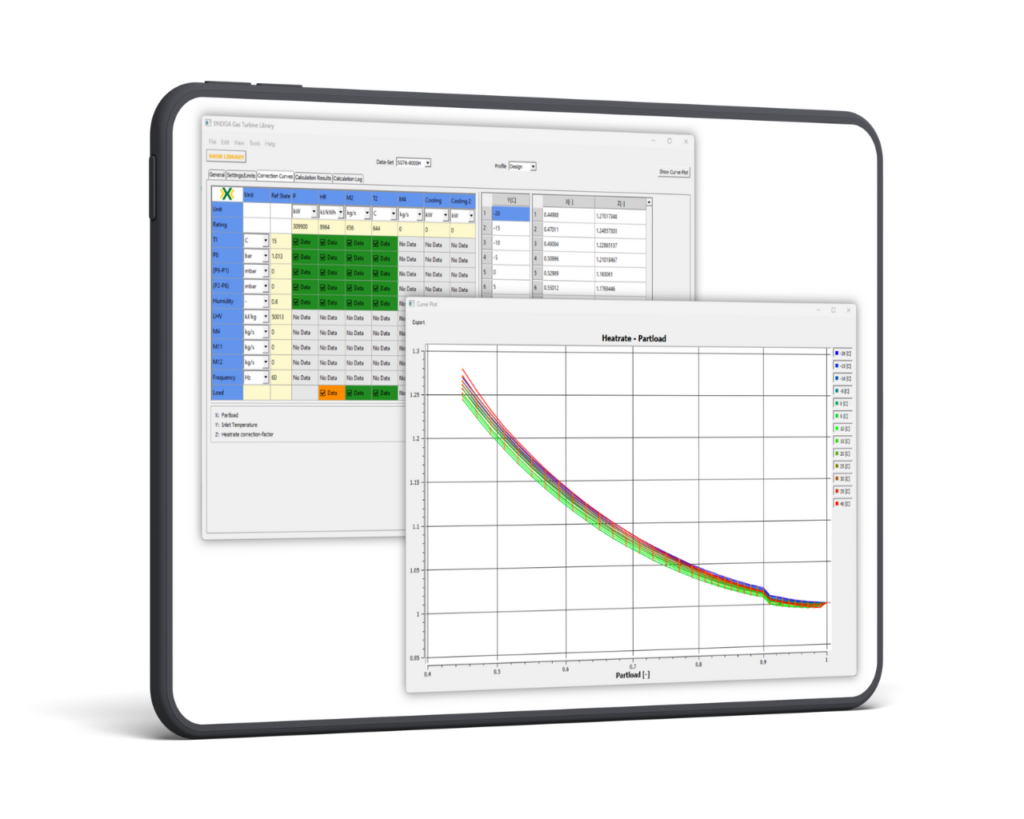
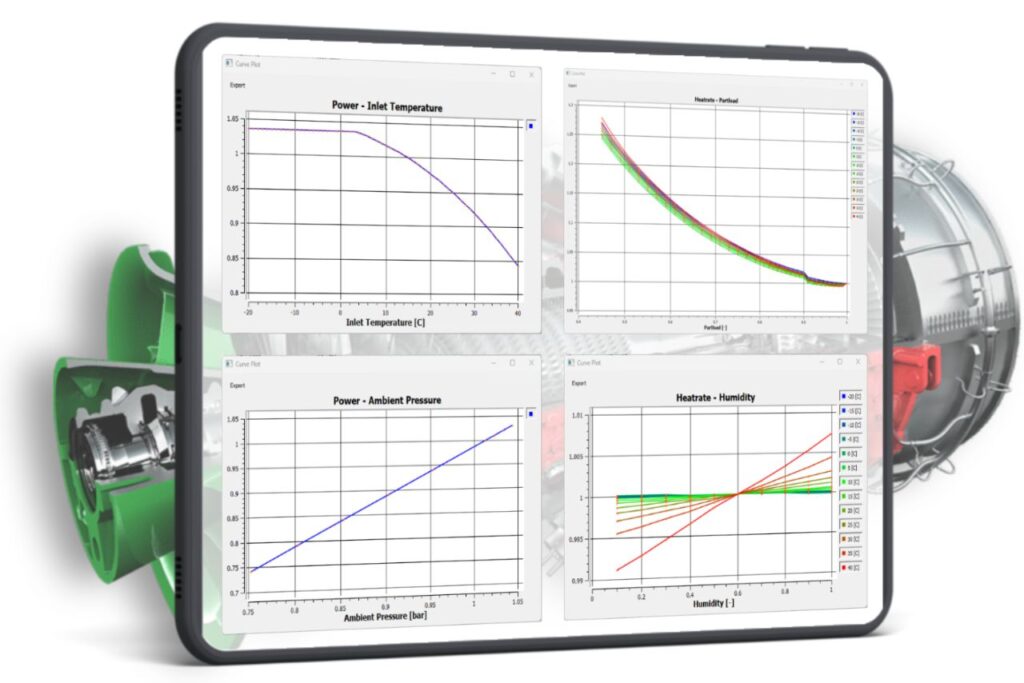
The Gas Turbine Library provides correction factors and offsets for power, heat rate, exhaust flow, exhaust temperature, cooling duties and injection flows in correlation to ambient and other operating conditions as well as part load operation. Up to 69 correction curves can be included in one data set for a specific GT model. The data are stored in tables that can be accessed in an easy-to-use and clear matrix of correction curves. The user can use the pre-configured and vendor approved curve sets provided by ENEXSA. It is also possible to create a new data set based on project-specific information from scratch or by copying and editing existing data sets.
Depending on the nature of the performance correlation, the correction Curves are one- or two-dimensional. Each Correction Curve can be displayed separately, and individual values of the secondary parameter can be selected or de-selected. The example shown here is a typical curve for heat rate vs. part load fraction, with ambient temperature as the secondary parameter.
The ENEXSA Reciprocating Engine Library is designed for the use within EBSILON®Professional Component 153 (Reciprocating Engine). This component is designed to represent large gas or diesel engines with heat integration. The performance data are supplied and approved by the respective OEM.
The combination of thermal performance data and detailed information about the control schemes for temperature and flow of the different cooling cycles within the gas engine is important for the simulation of a modern highly-integrated CHP plant. The engine model calculates the load-dependent amount of available waste heats which can be optimally utilized in the connected systems. This approach also allows the user to produce an exact digital twin of the plant which is valid over the entire operating range.
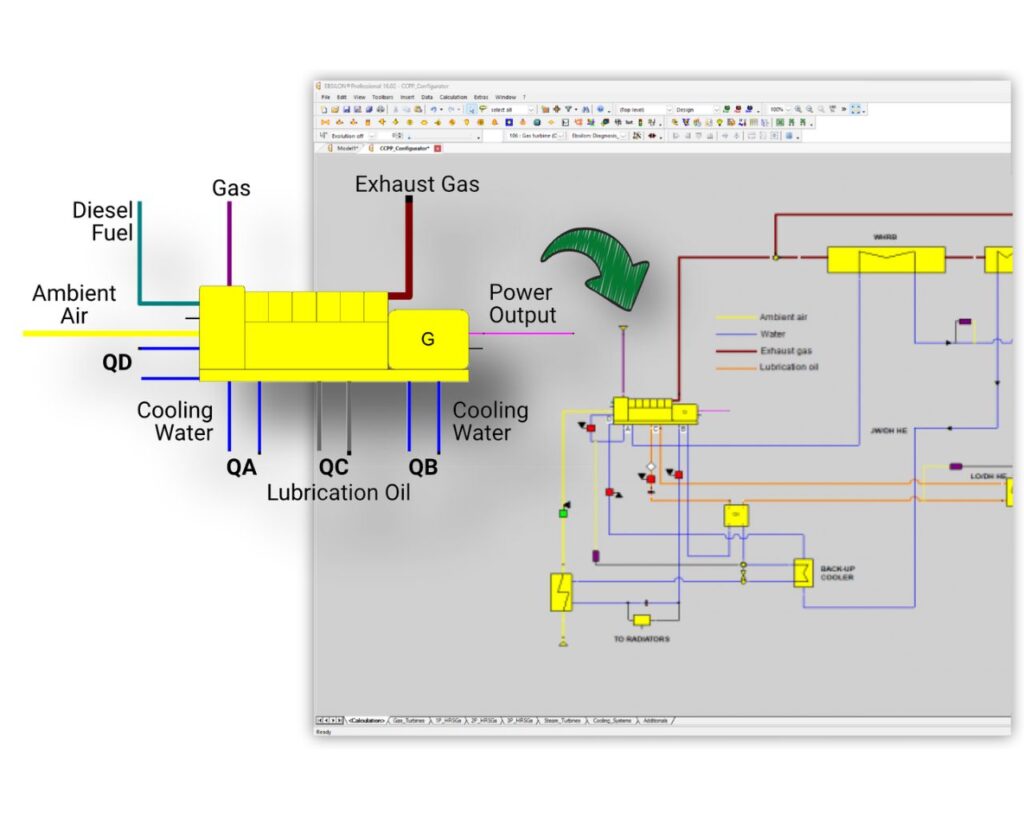
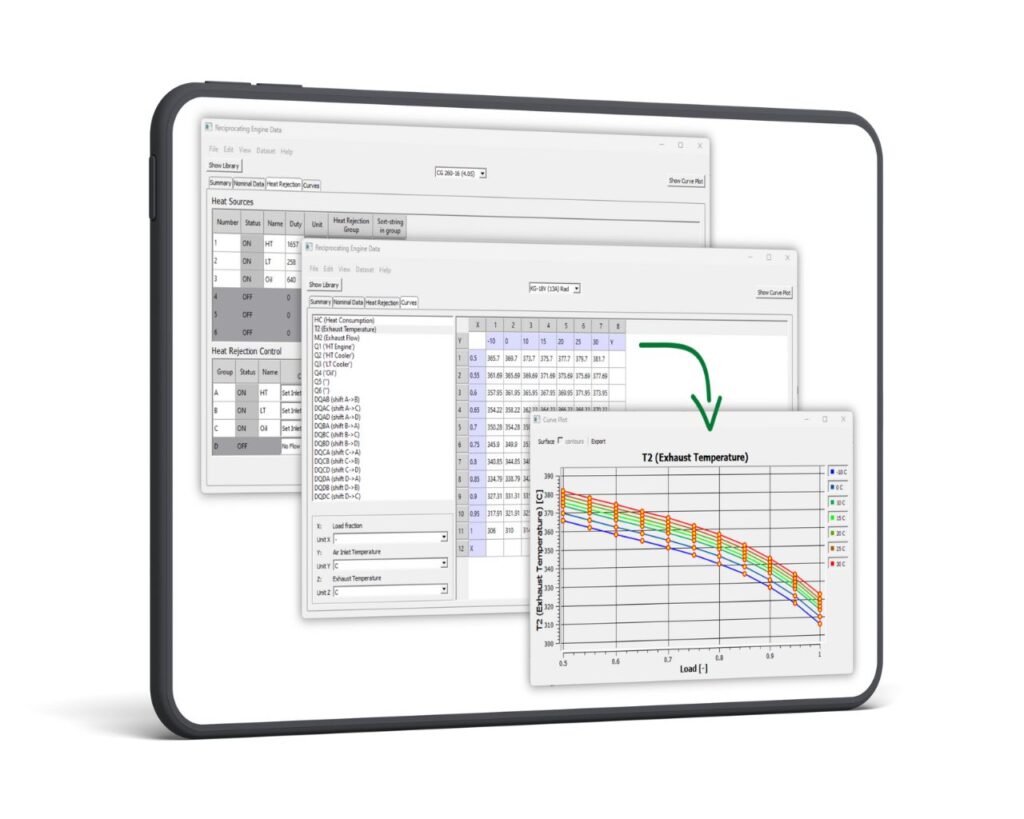
In order to reach maximum fuel efficiency, modern engine-based CHP plants aim at maximum integration of the waste heat available from the engine. To describe the individual heat items available from the engine, up to six heat sources can be defined, and the utilization of this heat is controlled in four different heat rejection groups. Multiple options for control schemes for flow and temperature of the different cooling cycles allow for accurate representation of the energy released from the engine, not only in terms of duty, but also in terms of flow and temperature. The latter is important for the correct simulation of the heat utilization, since these parameters may become limiting under specific operating conditions.
The ENEXSA Reciprocating Engine Library data sets describe power, heat consumption, exhaust temperature, exhaust flow and various heat sources (HT, LT, Oil, Jacket) with respective shift of heat as a function of temperature and load. The correlations are provided as two-dimensional matrices. The sample screen shot shows the correlation of exhaust temperature and engine load fraction with inlet temperature as the secondary parameter.
Explore our articles and other resources as a free download.
List of the included gas turbines in the ENEXSA gas turbine library.
List of the included gas reciprocating engines in the ENEXSA engine library.
The EBSILON gas turbine library is the best way to see the performance capability of your GT.
© ENEXSA GmbH | Imprint | Privacy Policy | Website: VISIONARY Consulting
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Wistia. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information